15 Oct What is Virtual Training? Tips & Examples
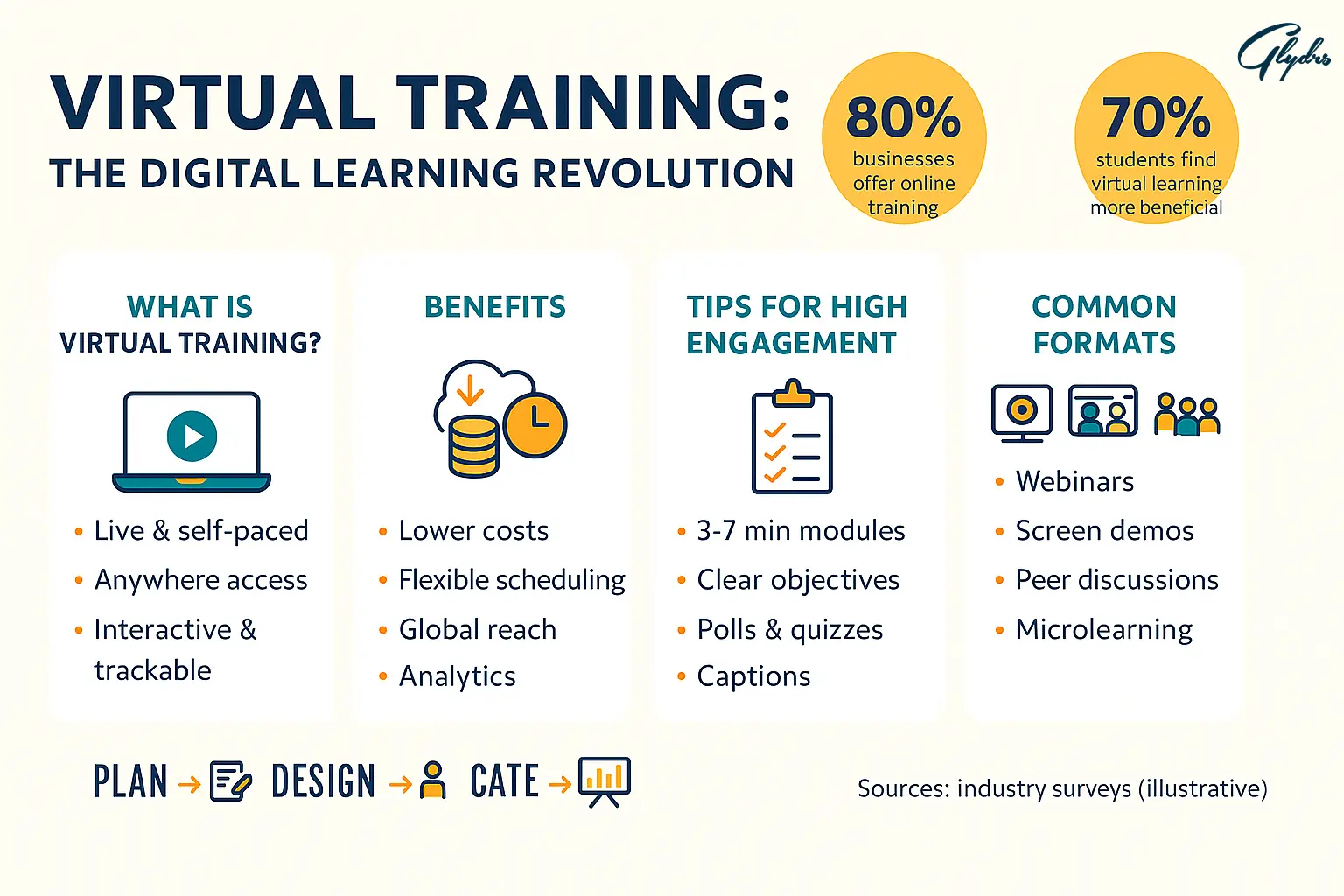
Virtual Training: The Digital Learning Revolution
You’ve witnessed one of the most dramatic shifts in modern education and professional development. The transition from traditional classroom settings to digital learning environments has fundamentally changed how training is delivered and received. This transformation accelerated exponentially during the global pandemic, but it’s clear that Virtual Training isn’t just a temporary solution—it’s become the backbone of modern learning strategies.
Consider these compelling statistics: 80% of businesses now offer online training materials, and 70% of students report finding virtual instruction more beneficial than traditional classroom learning. You’re not just adapting to a trend; you’re embracing a revolution that’s proven its effectiveness and staying power.
The shift to Virtual Training has eliminated geographical boundaries, reduced costs, and created unprecedented flexibility for learners and instructors alike. Whether you’re a corporate trainer looking to upskill your workforce, an educator seeking to reach more students, or a business owner wanting to streamline your training processes, understanding virtual training has become essential for your success.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about virtual training, from its fundamental principles to advanced implementation strategies. You’ll discover practical tips, real-world examples, and expert insights that will help you create engaging, effective virtual learning experiences.
What is Virtual Training?
Virtual Training represents a comprehensive learning experience conducted entirely in a digital environment. When you implement virtual training, you’re creating an online classroom where participants can acquire new skills, knowledge, and competencies without being physically present in the same location.
At its core, virtual training consists of both live and recorded sessions that can span from single-session workshops to multi-week comprehensive programs. You have the flexibility to design courses that include interactive video sessions, self-paced modules, collaborative discussions, and hands-on exercises—all delivered through digital platforms.
The beauty of virtual training lies in its ability to combine synchronous and asynchronous capabilities. Synchronous training means you’re conducting real-time sessions where all participants learn together simultaneously, often through video conferencing platforms. Asynchronous training allows learners to access content at their own pace, providing the ultimate flexibility for busy schedules.
When you compare Virtual Training to traditional classroom instruction, the differences become immediately apparent. Traditional training requires physical presence at a designated location, involves printed materials, and operates within fixed time constraints. Virtual training, however, transcends these limitations by leveraging technology to create dynamic, interactive learning environments accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
Real-world examples of virtual training in action include corporate onboarding programs delivered through video conferencing, interactive software tutorials conducted via screen sharing, virtual reality simulations for technical skills training, and gamified learning modules that engage participants through competitive elements. Healthcare professionals use virtual training for continuing education, financial institutions deliver compliance training remotely, and educational institutions offer entire degree programs online.
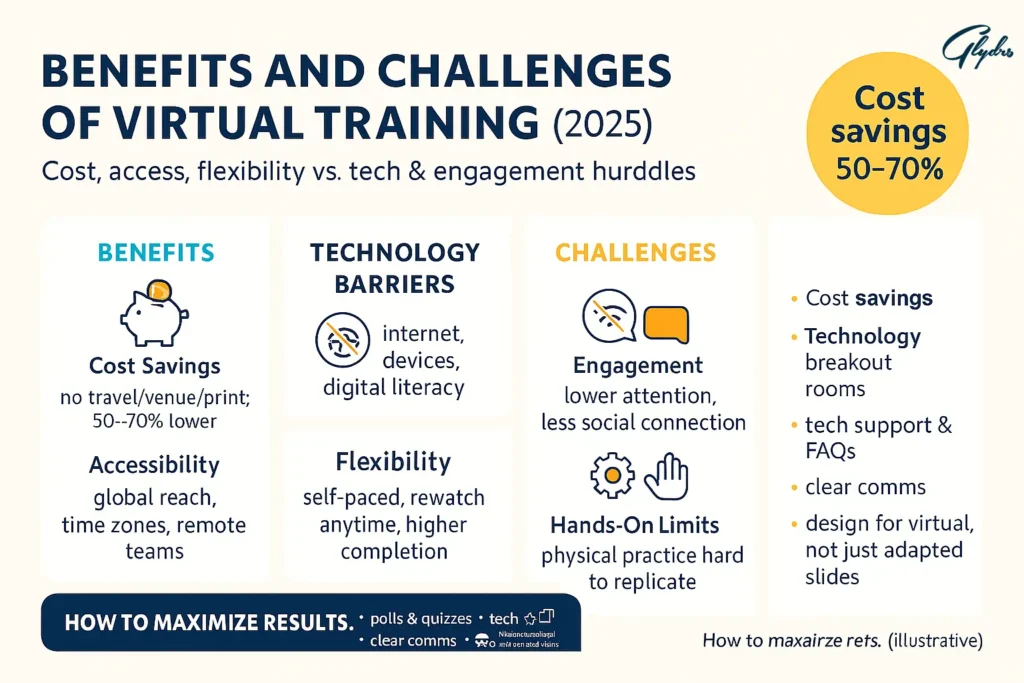
Benefits and Challenges of Virtual Training
When you implement Virtual Training, you’ll discover significant advantages that can transform your training approach. Cost savings represent one of the most compelling benefits—you’ll eliminate travel expenses, venue rentals, printed materials, and accommodation costs. These savings often reach 50-70% compared to traditional in-person training programs.
Accessibility becomes dramatically improved through virtual training. You can reach participants across different geographic locations, time zones, and even countries. This expanded reach means you’re no longer limited by physical proximity when selecting trainers or participants. Someone in London can easily learn from an expert based in New York, creating opportunities that simply weren’t feasible with traditional training methods.
Flexibility stands as another cornerstone benefit. Your participants can access training materials during their most productive hours, repeat sessions as needed, and balance learning with their existing work and personal commitments. This self-paced approach often leads to better knowledge retention and higher completion rates.
Scalability becomes effortless with virtual training.
You can train dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of participants simultaneously without the logistical nightmare of finding appropriately sized venues or coordinating complex scheduling arrangements.
However, Virtual Training does present certain challenges you’ll need to address. Technology barriers can create obstacles for participants who lack reliable internet connections, modern devices, or basic digital literacy skills. The digital divide remains a real concern that requires thoughtful solutions.
Engagement difficulties represent another significant challenge. Without face-to-face interaction, some participants may struggle to maintain attention, feel disconnected from the learning experience, or miss the spontaneous interactions that make traditional classroom learning memorable.
Reduced hands-on learning opportunities can limit certain types of training, particularly those requiring physical manipulation of tools, equipment, or materials. While virtual simulations continue improving, they can’t completely replicate every hands-on experience.
To maximize benefits while minimizing drawbacks, you should implement interactive elements like polls and breakout sessions, provide technical support resources, create clear communication channels, and design content specifically for the virtual environment rather than simply adapting in-person materials.
Types of Virtual Training Methods
Live webinars and video conferencing sessions represent the most interactive form of Virtual Training you can implement. These synchronous sessions allow real-time interaction between instructors and participants, enabling immediate questions, group discussions, and collaborative activities. You’ll find these particularly effective for complex topics requiring explanation, demonstration, or group problem-solving.
Self-paced e-learning modules offer maximum flexibility for your participants. These asynchronous courses allow learners to progress through materials at their preferred speed, revisit challenging concepts, and fit learning into their existing schedules. You can create comprehensive learning paths that guide participants through sequential topics while allowing individual pacing preferences.
Blended learning approaches combine the best of virtual and in-person elements. You might conduct virtual sessions for knowledge transfer and theoretical concepts, then follow up with hands-on workshops or practical applications in physical settings. This hybrid approach often provides the most comprehensive learning experience.
Interactive simulations and virtual labs create immersive learning environments where participants can practice skills without real-world consequences. These are particularly valuable for technical training, safety procedures, or complex process learning where mistakes in real environments could be costly or dangerous.
Gamification introduces competitive elements, reward systems, and game-like features to make learning more engaging. You can implement point systems, leaderboards, badges, and challenges that motivate participants to complete training modules and achieve higher performance levels.
Microlearning delivers content in small, digestible chunks that participants can consume quickly. These bite-sized modules work exceptionally well for just-in-time training, skill refreshers, or busy professionals who need to learn incrementally.
The key to success lies in matching the right method to your specific learning objectives, audience preferences, and content requirements. Complex technical subjects might benefit from interactive simulations, while policy updates could work well as microlearning modules.
Essential Tools and Technology for Virtual Training
Selecting the right video conferencing platform forms the foundation of successful Virtual Training delivery. Zoom offers robust features, including breakout rooms, screen sharing, recording capabilities, and interactive whiteboards. Its ability to handle large audiences with add-ons makes it suitable for enterprise-level training programs. The platform’s reliability and user-friendly interface have made it a popular choice across industries.
Microsoft Teams integrates seamlessly with Office 365 ecosystems, making it ideal if your organization already uses Microsoft products. Teams provides excellent file sharing through SharePoint integration, persistent chat capabilities, and strong security features that many corporations require. The platform supports both scheduled and impromptu training sessions effectively.
Google Meet offers simplicity and accessibility for organizations embedded in Google’s ecosystem. Its automatic captioning features can improve accessibility, while its integration with Google Workspace tools streamlines content sharing and collaboration.
Learning Management Systems (LMS) serve as the central hub for your virtual training programs.
These platforms allow you to organize course content, track participant progress, deliver assessments, and generate detailed reports. Popular LMS options include Moodle for customization flexibility, Canvas for user experience, and Blackboard for comprehensive enterprise features.
Content creation and authoring tools enable you to develop engaging training materials. Applications like Articulate Storyline, Adobe Captivate, and Camtasia help you create interactive presentations, video tutorials, and multimedia-rich learning experiences that keep participants engaged throughout their learning journey.
Interactive whiteboards and collaboration platforms such as Miro, Jamboard, or Conceptboard facilitate group brainstorming, visual learning, and collaborative exercises. These tools replicate the collaborative aspects of physical whiteboards while adding digital capabilities like saving, sharing, and real-time multi-user editing.
Assessment and quiz platforms like Kahoot, Poll Everywhere, or built-in LMS assessment tools help you measure learning effectiveness, maintain engagement through interactive quizzes, and provide immediate feedback to participants.
Hardware requirements include reliable high-speed internet connections, quality webcams and microphones for clear audio-visual communication, and devices capable of running your chosen software platforms smoothly. Consider providing technical specifications to participants well before training begins.
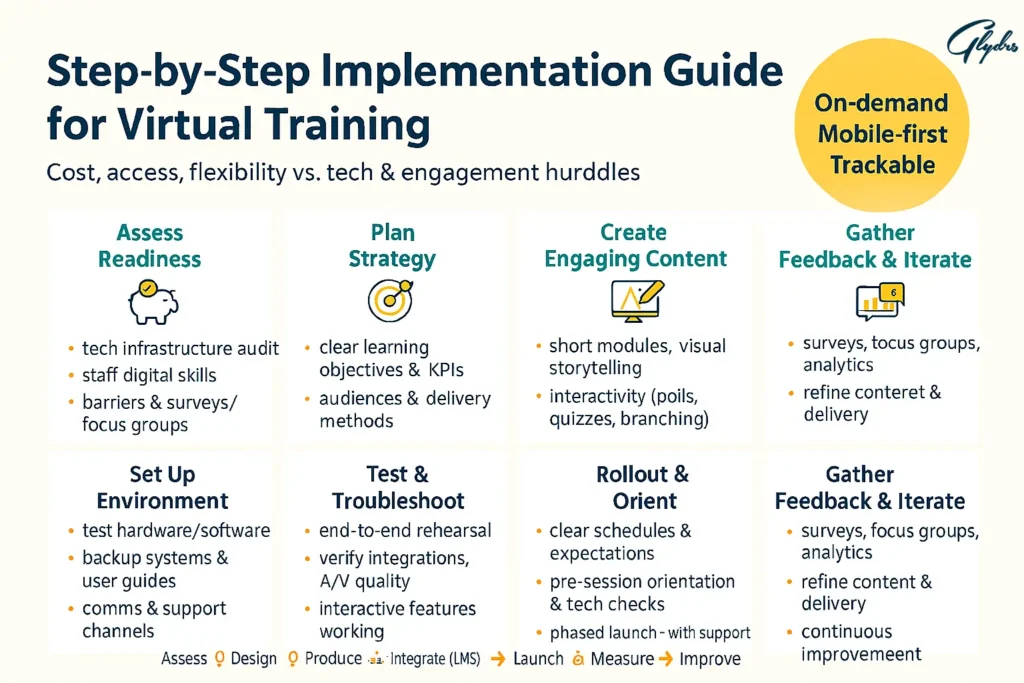
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
Assessing organizational readiness for Virtual Training requires an honest evaluation of your current capabilities, resources, and constraints. You’ll need to examine your existing technology infrastructure, evaluate staff technical competencies, and identify potential barriers to successful implementation. Consider conducting surveys or focus groups to understand your audience’s comfort level with digital learning platforms.
Planning your virtual training strategy involves defining clear learning objectives, identifying your target audience, determining appropriate delivery methods, and establishing success metrics. You should create detailed timelines, allocate necessary resources, and develop contingency plans for potential challenges. Consider how virtual training aligns with your broader organizational goals and learning culture.
Selecting the right technology stack requires careful consideration of your specific needs, budget constraints, and integration requirements. Evaluate different platforms based on features, scalability, user experience, technical support, and cost. Don’t forget to consider factors like security requirements, accessibility features, and mobile compatibility.
Creating engaging virtual content demands a different approach than traditional materials. You’ll need to design shorter content segments, incorporate interactive elements, use varied multimedia formats, and build in regular engagement checkpoints. Focus on visual storytelling, clear audio quality, and logical content flow that works well in digital environments.
Setting up your virtual training environment involves testing all technology components.
preparing backup systems, creating user guides and technical support resources, and establishing communication protocols. You should conduct thorough rehearsals, prepare troubleshooting procedures, and ensure all participants have the necessary access credentials and technical specifications.
Testing and troubleshooting before launch prevents embarrassing technical failures and participant frustration. Run complete system tests, verify all integrations work properly, check audio and video quality, and confirm that all interactive features function correctly. Have technical support readily available during initial sessions.
Rolling out training programs effectively requires clear communication about expectations, schedules, and technical requirements. Provide participants with pre-session orientations, technical check opportunities, and easy access to support resources. Consider phased rollouts that allow you to refine processes based on early feedback.
Gathering feedback and iterating ensures continuous improvement of your Virtual Training programs. Implement regular feedback collection through surveys, focus groups, and informal check-ins. Use this information to refine content, adjust delivery methods, and enhance the overall learning experience.
Best Practices and Expert Tips with Real Examples
Designing engaging and interactive virtual content requires understanding how attention spans differ in digital environments. You should break content into 10-15 minute segments with interactive elements between each section. A leading technology company successfully transformed its 8-hour compliance training into a series of 20-minute modules with gamified quizzes, resulting in 85% completion rates compared to 45% for their previous full-day sessions.
Maintaining participant attention throughout virtual sessions demands proactive engagement strategies. Use polls every 10-15 minutes, implement breakout room discussions, and encourage chat participation through specific prompts. A healthcare organization found that incorporating “movement breaks” every 30 minutes—asking participants to stand and perform simple stretches—significantly improved focus and retention rates.
Creating a strong instructor presence in virtual environments requires intentional techniques that may feel unnatural initially. Maintain eye contact with the camera rather than the screen, use gestures and facial expressions deliberately, and speak with slightly more energy than you would in person. A successful corporate trainer increased their virtual session ratings from 3.2 to 4.7 out of 5 by implementing these presence techniques and regularly using participants’ names during discussions.
Encouraging collaboration and networking in virtual settings requires structured approaches.
Design specific networking activities like virtual coffee chats, implement collaborative projects using shared digital workspaces, and create discussion forums for ongoing interaction. A professional development organization increased participant satisfaction by 40% after introducing “virtual networking lounges” where participants could join informal discussions before and after formal sessions.
Managing different time zones and schedules presents unique challenges for global Virtual Training initiatives. Record all live sessions for asynchronous access, rotate meeting times to share inconvenience fairly, and provide multiple options for key training components. A multinational corporation solved its timezone challenges by delivering core content through recorded modules and offering live Q&A sessions at different times throughout the week.
Providing technical support and backup plans prevents minor issues from becoming major disruptions. Create detailed troubleshooting guides, establish dedicated support channels during training sessions, and prepare alternative delivery methods for critical content. A financial services firm reduced technical-related session interruptions by 90% after implementing a “tech buddy” system where technically proficient participants assisted others with minor issues.
Industries Leading Virtual Training Adoption
The education sector has undergone the most dramatic transformation in Virtual Training adoption. Universities now offer entire degree programs online, K-12 schools have integrated virtual learning into standard curricula, and continuing education providers have expanded their global reach exponentially. The University of Arizona, for example, saw its online enrollment increase by 300% while maintaining educational quality through innovative virtual labs and collaborative learning platforms.
Healthcare training has embraced virtual reality and simulation technologies to provide safe learning environments for high-stakes procedures. Medical schools use VR simulations for surgical training, nursing programs employ virtual patient scenarios, and continuing medical education has moved largely online. The Cleveland Clinic developed virtual training programs that reduced training time for new procedures by 40% while improving competency scores.
Corporate and business training has evolved from conference room presentations to sophisticated virtual learning ecosystems. Companies now deliver leadership development, technical skills training, and compliance education through comprehensive virtual programs. IBM transformed its global training approach, moving 90% of its employee development online and reducing training costs by $300 million annually while improving learning outcomes.
Financial services organizations have leveraged virtual training for regulatory compliance.
customer service excellence, and technical skills development. The complex nature of financial regulations makes virtual training particularly valuable for consistent message delivery and comprehensive documentation. JPMorgan Chase implemented virtual compliance training that ensures consistent delivery across 60 countries while reducing compliance violations by 25%.
Manufacturing companies use virtual training for safety procedures, equipment operation, and quality control processes. Virtual simulations allow workers to practice with expensive machinery without risk of damage or injury. Boeing reduced aircraft manufacturing training time by 25% through virtual assembly line simulations while improving safety scores and reducing equipment damage during training.
Government and public sector organizations have adopted virtual training for citizen services, emergency response procedures, and administrative functions. The flexibility of virtual training helps government agencies deliver consistent training across geographically dispersed locations while managing budget constraints effectively.
Keep reading and uncover secrets that can change the way you work. Top 10 E-Learning Production Companies in the USA 2025
Measuring Success and ROI of Virtual Training
Completion rates serve as a fundamental metric for Virtual Training effectiveness. Unlike traditional training, where physical attendance guarantees exposure to content, virtual training requires active participation for learning to occur. You should track not just initial enrollment but also module completion, assessment participation, and certificate achievement. Benchmark completion rates typically range from 60-80% for mandatory corporate training and 15-30% for voluntary professional development programs.
Engagement metrics provide deeper insights into training quality and participant experience. Monitor session attendance duration, chat participation rates, poll responses, and interactive element usage. High engagement often correlates with better learning outcomes and higher satisfaction scores. Track metrics like average session attendance time, number of questions asked, and participation in optional activities.
Learning assessment and skill application measurement determine whether training objectives are being met. Implement pre- and post-training assessments, conduct follow-up evaluations after participants return to work, and measure behavioral changes in job performance. Use varied assessment methods, including quizzes, practical demonstrations, peer evaluations, and supervisor feedback.
Cost comparison analysis
With traditional training reveals the financial impact of your virtual training investments. Calculate direct savings from eliminated travel, venue, and material costs, but also consider indirect benefits like reduced time away from work, increased training frequency, and expanded participant reach. Many organizations see 40-60% cost reductions when transitioning to virtual formats.
Long-term impact tracking evaluates the sustained effectiveness of your training programs. Measure knowledge retention at 30, 60, and 90-day intervals, track job performance improvements, monitor promotion rates among trained employees, and assess skill application in real work situations. This longitudinal data helps justify training investments and identify areas for improvement.
Tools and methods for ongoing assessment include learning management system analytics, survey platforms for participant feedback, performance management system integration, and business intelligence dashboards for comprehensive reporting. Automated data collection reduces administrative burden while providing more consistent measurement.
Creating reports for stakeholders requires translating training metrics into business language that demonstrates value. Focus on business outcomes like improved productivity, reduced errors, faster onboarding times, and enhanced compliance scores rather than just training completion statistics.
Keep reading and uncover secrets that can change the way you work. Corporate Training: Definition, Types & Benefits (2025)
The Future of Virtual Training
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing Virtual Training through personalized learning paths that adapt to individual learning styles, paces, and preferences. AI algorithms analyze participant performance, identify knowledge gaps, and automatically adjust content difficulty and presentation methods. Predictive analytics help identify participants at risk of falling behind, enabling proactive intervention and support.
Machine learning enables intelligent content recommendations, automated assessment grading, and natural language processing for improved virtual assistant capabilities. Chatbots provide 24/7 support for common training questions, while AI-powered analytics identify optimal training schedules and content sequences for maximum effectiveness.
Virtual and augmented reality integration is creating immersive learning experiences that were impossible with traditional methods. VR simulations allow safe practice of dangerous procedures, AR overlays provide real-time guidance during equipment operation, and mixed reality environments enable collaborative learning in virtual spaces that feel remarkably realistic.
Mobile-first training approaches recognize
That learners increasingly access content through smartphones and tablets. Responsive design, offline content access, push notifications for learning reminders, and micro-learning modules optimized for mobile consumption are becoming standard expectations rather than nice-to-have features.
Blockchain technology may revolutionize credential verification and skill certification, creating secure, verifiable records of learning achievements that learners own and control. Smart contracts could automate compliance training requirements and renewal processes.
Social learning platforms are incorporating elements from social media to increase engagement and peer-to-peer learning. Features like learning communities, peer mentoring, social recognition systems, and collaborative content creation are becoming integral parts of comprehensive virtual training ecosystems.
Preparing for upcoming trends requires staying informed about technological developments, experimenting with emerging tools and platforms, and maintaining flexibility in your training technology investments. Focus on platforms and approaches that can adapt and integrate with future innovations rather than proprietary systems that might become obsolete.
Keep reading and uncover secrets that can change the way you work. The Ultimate Guide to Supervisor Training Topics
Your Virtual Training Success Starts Here
You now possess a comprehensive understanding of Virtual Training and its transformative potential for your organization. The journey from traditional classroom instruction to sophisticated virtual learning environments represents more than just a technological upgrade—it’s a fundamental shift toward more accessible, flexible, and effective education delivery.
The evidence is clear: virtual training offers compelling advantages in cost savings, accessibility, scalability, and learner satisfaction when implemented thoughtfully. You’ve learned about the essential tools, implementation strategies, and best practices that separate successful virtual training programs from those that struggle to engage participants effectively.
Your immediate next steps should focus on assessing your organization’s readiness, selecting appropriate technology platforms, and designing content specifically for virtual environments. Remember that successful Virtual Training requires different approaches than simply moving in-person content online—you need to embrace the unique capabilities and characteristics of digital learning environments.
Start small with pilot programs that allow you to test approaches, gather feedback, and refine your methods before scaling up to larger initiatives. Build internal expertise gradually, invest in quality content creation, and prioritize participant experience above all else.
The future of learning is increasingly virtual, and early adopters who master these approaches will have significant competitive advantages in workforce development, customer education, and knowledge transfer. You have the tools and knowledge needed to begin this transformation—now it’s time to take action and create virtual training experiences that truly make a difference.
Turn your goals into real achievements with our tailored services – request the service now.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What’s the difference between virtual training and online learning?
While these terms are often used interchangeably, virtual training typically refers to more structured, instructor-led programs that simulate traditional classroom experiences through video conferencing and real-time interaction. Online learning is a broader category that includes self-paced courses, recorded content, and automated learning systems. Virtual training emphasizes live interaction and immediate feedback, while online learning may be entirely asynchronous. Both approaches can be highly effective depending on your learning objectives and audience preferences.
How much does virtual training cost compared to in-person training?
Virtual Training typically costs 40-60% less than equivalent in-person programs when you factor in all expenses. Direct savings come from eliminated travel costs, venue rentals, printed materials, and accommodation expenses. Indirect savings include reduced time away from work, lower instructor travel costs, and the ability to reach more participants per session. However, initial setup costs for technology platforms, content development, and equipment should be considered. Most organizations see positive ROI within 6-12 months of implementation.
What technical skills do instructors need for virtual training?
Instructors need basic proficiency with video conferencing platforms, screen sharing capabilities, and file management systems. More advanced skills include using interactive whiteboards, managing breakout rooms, conducting polls and quizzes, and troubleshooting common technical issues. Soft skills become equally important—virtual instructors must project energy and enthusiasm more deliberately. Engage participants proactively, and manage time effectively in digital environments. Most instructors can develop these competencies through practice and targeted training programs.
How do you handle technical issues during virtual sessions?
Successful virtual training requires proactive technical support strategies. Create detailed troubleshooting guides for common issues, establish dedicated support channels during sessions. And prepare backup delivery methods for critical content. Have participants test their technology before sessions, provide multiple ways to access content, and designate tech-savvy participants as peer supporters. Always have phone numbers available for audio backup when internet connections fail. And record sessions so participants can catch up on missed content.
Can virtual training be as effective as face-to-face training?
Research consistently shows that well-designed Virtual Training can be equally or more effective than in-person training for knowledge transfer and skill development. Virtual training often provides better accessibility, allows for more personalized pacing, and can incorporate interactive elements that enhance engagement. However, effectiveness depends heavily on design quality, instructor competence, and appropriate technology use. Some hands-on skills may still require in-person components. But the majority of corporate and educational training objectives can be achieved effectively through virtual methods.
What are the best practices for engaging remote learners?
Engaging remote learners requires intentional design and active facilitation. Use interactive elements like polls and breakout discussions every 10-15 minutes, encourage chat participation through specific prompts. And incorporate movement breaks to maintain physical engagement. Create opportunities for peer interaction, use participants’ names frequently, and provide multiple ways to participate (audio, chat, polls). Keep content segments short and focused, use high-quality visuals and multimedia. And follow up with participants individually when possible to maintain personal connections.


No Comments